Variety Mails
Tuesday, June 16, 2020
Tuesday, October 13, 2015
Profesionals...............
Pharmacists
Pharmacists are health professionals who practice the art and science of pharmacy. In their traditional role, pharmacists typically take a request for medicines from a prescribing health care provider in the form of a medical prescription and dispense the medication to the patient and counsel them on the proper use and adverse effects of that medication. In this role, pharmacists ensure the safe and effective use of medications. Pharmacists also participate in disease state management, where they optimise and monitor drug therapy – often in collaboration with physicians and/or other health professionals. Pharmacists have many areas of expertise and are a critical source of medical knowledge in clinics, hospitals, and community pharmacies throughout the world.
Pharmacists are sometimes small-business owners, owning the pharmacy in which they practice. They are also very skilled and specialized individuals with specific knowledge that makes them a vital part of any healthcare team. They act as a learned intermediary between patients and other healthcare providers to ensure that proper medical therapy is chosen and implemented in the best way possible.
Pharmacists are sometimes referred to as chemists (or dispensing chemists), which sometimes causes confusion with scientists in the field of chemistry. This term is a historical one, since pharmacists originally were required to complete an undergraduate degree in Pharmaceutical Chemistry (PhC) and were known as "Pharmaceutical Chemists".
Skills and roles
Pharmacists are exceptionally trained in medicine-related fields including pharmacology, chemistry, pharmaceutical chemistry, pharmacy practice (including drug interactions, medicine monitoring, medication management), pharmaceutics, pharmacy law, physiology, anatomy, biochemistry, kinetics, nephrology, hepatology, and compounding medications. Additional curriculum covers basic diagnosis with emphasis on disease state management, therapeutics and prescribing (selecting the most appropriate medication for a given patient).
Pharmacists are often the first point-of-contact for patients with health inquiries. This means that pharmacists have large roles in the primary care of patients. These roles may include, but are not limited to:
clinical medication management
the assessment of patients with undiagnosed or diagnosed conditions and for decisions about the clinical management required, including prescribing
specialized monitoring of simple and complex disease states
reviewing medication regimens
monitoring of treatment regimens
general health monitoring
compounding medicines
general health advice
providing specific education to patients about disease states and medications
oversight of dispensing medicines on prescription
provision of non-prescription medicines
counseling and advice on optimal use of medicines
advice and treatment of common ailments
referral to other health professionals if necessary
dosing drugs in renal and hepatic failure
pharmacokinetic evaluation
education of physicians and other healthcare providers on medications and their proper use
prescribing medications in collaboration with other healthcare professionals
providing pharmaceutical information
promoting public health by administering immunizations
Free Download Medical Dictionary - MediDict

Click Here To Download MediDict
Click Here To Download MediDict
About MediDict
MediDict is an offline medical Dictionary offers you the opportunity to search medicines and Drugs. It helps you to clear your doubts regarding classes and varieties of medicines. It contains about 761 different drugs and its therapeutic and pharmacologic classification. You can search drug ways search and on the basis of the pharmacological classification ways.
Click here to Downlaod the MediDict
About Author
Rahul Soman, M. Pharm., Pharmaceutics is the author of MediDict. Visit my blogs,
How to Use
MediDict is an offline medical Dictionary offers you the opportunity to search medicines and Drugs. It helps you to clear your doubts regarding classes and varieties of medicines. It contains about 761 different drugs and its therapeutic and pharmacologic classification. You can search drug ways search and on the basis of the pharmacological classification ways.
Click here to Downlaod the MediDict






Free Download Medical Dictionary - MediDict

Click Here To Download MediDict
Click Here To Download MediDict
About MediDict
MediDict is an offline medical Dictionary offers you the opportunity to search medicines and Drugs. It helps you to clear your doubts regarding classes and varieties of medicines. It contains about 761 different drugs and its therapeutic and pharmacologic classification. You can search drug ways search and on the basis of the pharmacological classification ways.
Click here to Downlaod the MediDict
About Author
Rahul Soman, M. Pharm., Pharmaceutics is the author of MediDict. Visit my blogs,
How to Use
MediDict is an offline medical Dictionary offers you the opportunity to search medicines and Drugs. It helps you to clear your doubts regarding classes and varieties of medicines. It contains about 761 different drugs and its therapeutic and pharmacologic classification. You can search drug ways search and on the basis of the pharmacological classification ways.
Click here to Downlaod the MediDict






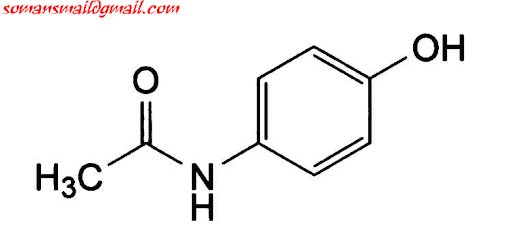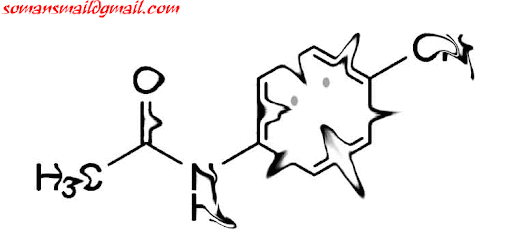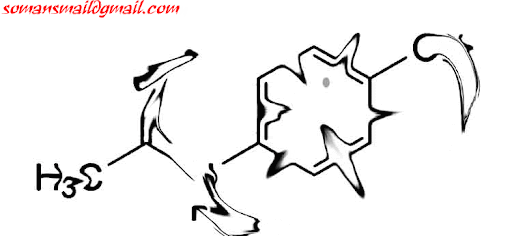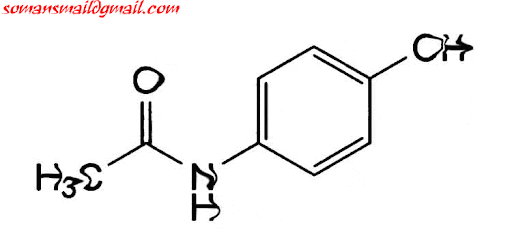
Mind Just before Medicinal Chemistry Exam
A to Z about Diseases
Acne vulgaris
Acute lymphoid leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia
AIDS
Alopecia
Alzheimer
Anaphylaxis
Anemia
Anemia - Megaloblastic
Anemia – Sickle Cell
Anemia (Hemolytic)
Anemia (Iron Deficiency)
Anemia (Megaloblastic - vitamin B12 deficiency
Anemia Megaloblastic - folate deficiency
Ankylosing spondylitis
Anthrax
Aplastic anemia
Appendicitis
Arthritis – Rheumatoid
Arthritis (Juvenile Idiopathic)
Atrophy
Autism
Autistic disorder
Avian influenza
B
Bacterial meningitis
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
Bipolar disorder
Bird Flue
Botulism
Botulism (Infant)
Breast cancer
Bronchitis
Brucellosis
C
Cerebral palsy
Cervical cancer
Chalazion
Chancroid
CHF
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Chronic myeloid leukemia
Cluster headache
Colorectal cancer
CondylomaCongestive heart disease
Congestive Heart failure
D
Dementia
Diabetes mellitus
Diarrhea
Diphtheria
DM
E
Eclampsia
Encephalitis due to human herpes simplex virus
Esophageal cancer
F
Fatigue
G
Gastric cancer
Goiter
H
Hashimoto thyroiditis
Head and neck cancer
Heart failure
Hemolytic anemia
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C
HIV infection
Hodgkin's disease
Huntington's disease
Hypertension
Hypothermia
I
Infant botulism
Iritis
Iron deficiency anemia
Iron deficiency anemia
Irritable bowel syndrome
J
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
L
Legionella infection
Leishmaniasis
Lung cancer
Lyme disease
M
Malaria
Malignant tumor of thyroid gland
Malignant tumor of urinary bladder
Measles
Mediastinal emphysema
Megaloblastic Anemia
Megaloblastic anemia due to folate deficiency
Megaloblastic anemia- vitamin B12 deficiency
Meningitis
Meningitis- Viral
Migraine
Migraine
Multiple myeloma
Mumps
Muscular dystrophy
Myasthenia gravis
Myxedema coma
N
Nongonococcal cervicit
Nongonococcal urethritis
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Novel influenza A
O
Obesity
Obstructive sleep apnea
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis
Ovarian cancer
P
Pancreatic cancer
Parkinson's disease
Pertussis
Poliomyelitis
poliomyelitis
Polymyalgia rheumatica
Portal hypertension
Post poliomyelitis syndrome
Primary bone cancer
Primary bone cancer
Primary brain cancer
Primary brain cancer
Prolactinoma
Prostate cancer
Prostatitis
Psoriasis
Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary hypertension
Q
R
Rabies
Rheumatic fever
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rubella
S
SARS
Schizophrenia
Scleroderma
Seasonal influenza
Sepsis
Severe acute respiratory syndrome
Sickle cell anemia
Spinal Muscular Atrophy
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Streptococcal pharyngitis
Syphilis
Systemic lupus erythematosus
T
Temporal arteritis
Testicular cancer
Thyroid gland - Cancer
U
Urinary bladder - Cancer
Uterine cancer
V
Viral encephalitis
Viral Meningitis
Viral meningitis
- Gout and Hyperurecemia
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Acute coronary Syndroms
- Arrhymias
- Cardiopulmanary Resuscitation
- Heart Failure
- Hypertension
- Hyperlipidemia
- Ischemic Heart Diseases
- Shock
- Stroke
- Venous Thromboembolism
- Cirrhosis
- Portal Hypertension
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Gastroesophagal Reflux Disease
- Hepatitis, Viral
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Pancreatitis
- Peptic Ulcer disease
- Contraception
- Hormone therapy
- Central Nervous System infections
- Endocarditis
- Fungal infections, Invasive
- Gastrointestinal Infection
- HIV / AIDS
- Intra-Abdominal Infection
- Respiratory Tract infections, Lower
- Respiratory Tract infections, Upper
- Sepsis and Septic Shock
- Sexually transmited Diseases (STD)
- Skin and soft tissue infection
- Tuberculosis
- Urinary tract infection and prostatitis
- Epilepsy
- Headache
- Pain management
- Parkinson’s Diseases
- Status epilepticus
- Enteral Nutrition
- Obesity
- Parentaral Nutrition
- Breast cancer
- Colorectal Cancer
- Lung cancer
- Lymphomas
- Prostate cancer
- Cervical Cancer
- Esophageal Cancer
- Gastric Cancer
- Head and Neck Cancer
- Lung Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Primary bone Cancer
- Primary Brain cancer
- Testicular Cancer
- Thyroid Gland Cancer
- Urinar Bladder cancer
- Uterine Cancer
- Glaucoma
- Alzhimer’s Diseases
- Anxiety Disease
- Bipolar Diseases
- Depressive diseases
- Schizophrenia
- Sleep Diseases
- Substance-Related Diseases
- Acid base Diseases
- Acute renal Failure
- Chronic Renal Failure
- Drug Dosing in renal insufficiency
- Electrolyte Homeostasis
- Allergic Rhinitis
- Asthma
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases
- Benign Prostatic, Hyperplasia
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Urinary Incontinence






